- Published on
Visualising a Raspberry Pi Kubernetes cluster by deploying the k8s web interface
- Authors

- Name
- Peter Peerdeman
- @peterpeerdeman
A Kubernetes cluster is quite an abstract piece of software running on our new raspberry pi hardware cluster. Let's get some insight in all of the moving pieces such as nodes, pods, services, and volumes using the Kubernetes Web Interface.
First, we deploy the Dashboard UI using a deployment yaml from the kubernetes repository (check the latest version here
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/dashboard/v2.7.0/aio/deploy/recommended.yaml
Before we can access the deployment, we need to create a user and generate an access token, that we will use in our browser later on. This is detailed in the official guide. Create a file called service-account-token.yml, and copy in the following content and deploy this configuration with kubectl apply -f service-account-token.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: admin-user
namespace: kubernetes-dashboard
annotations:
kubernetes.io/service-account.name: "admin-user"
type: kubernetes.io/service-account-token
When the secret is created, you can retrieve the plaintext for the bearer token with the following command that automatically decodes the credential, since credentials are always base64 encoded in Kubernetes.
kubectl get secret admin-user -n kubernetes-dashboard -o jsonpath={".data.token"} | base64 -d
To access any service on the cluster with our browser, we need to create a local proxy that routes requests to the correct pod running our web interface.
kubectl proxy
http://localhost:8001/api/v1/namespaces/kubernetes-dashboard/
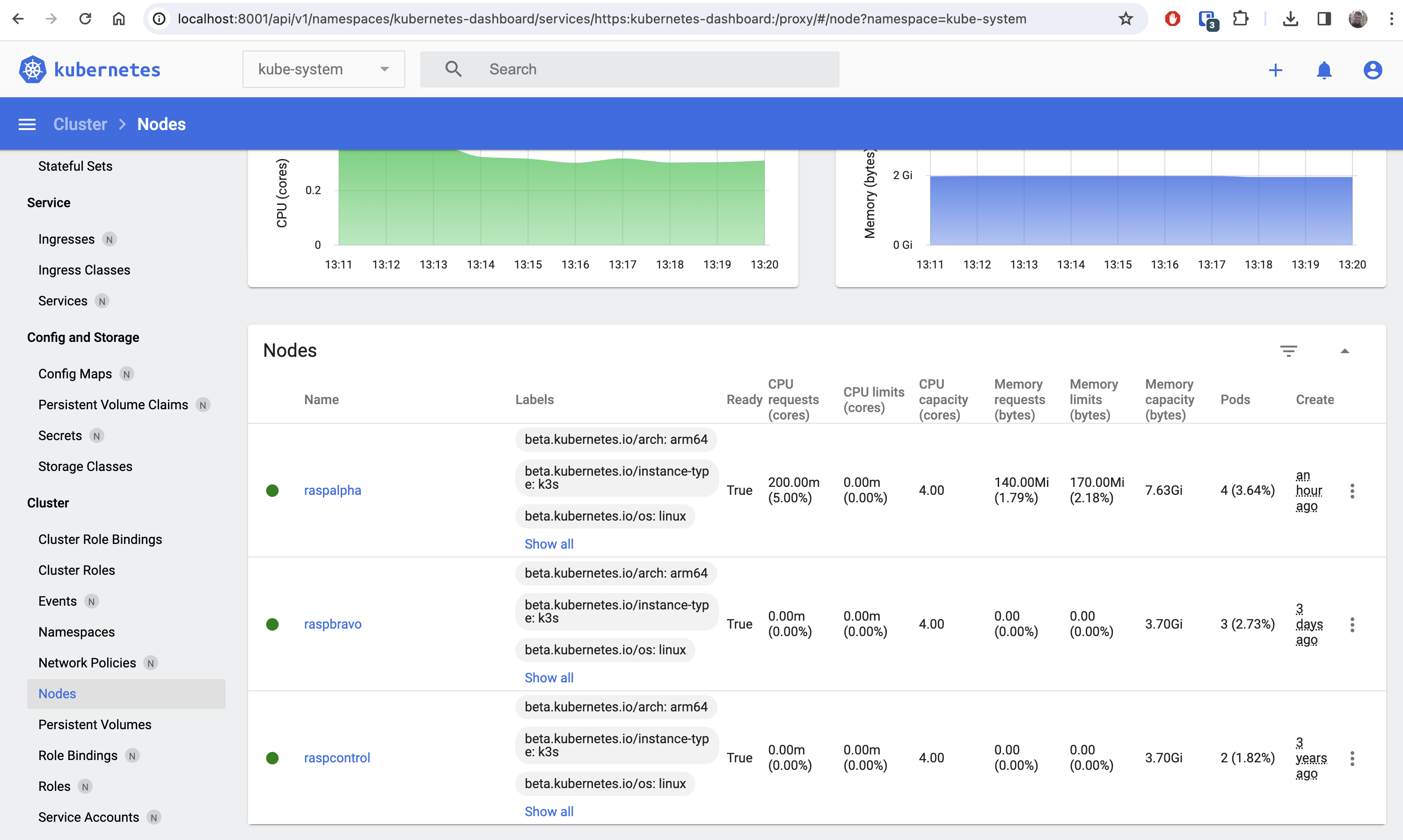
Use the plaintext bearer token you just retrieved in the interface and look at that, you can finally see what the heck is happening under the hood! Be sure to click around in the "kube-system" namespace dropdown on top.
Check the other blogs in this raspberry pi kubernetes cluster series here:
- Kubernetes cluster build with Raspberry Pi nodes and PoE Hats in a DIN breaker box panel
- Visualising a Raspberry Pi Kubernetes cluster by deploying the k8s web interface
- Longhorn for persistant, replicated storage on raspberry pi kubernetes cluster
- Deploying monitoring TIG stack (Telegraf, InfluxDB and Grafana) on Raspberry Pi Kubernetes cluster
- Deploying a NodeJS Postgres application to a Kubernetes Raspberry Pi Cluster
- Manage SSL certificates and ingress for services in k3s kubernetes cluster using cert-manager, letsencrypt and traefik